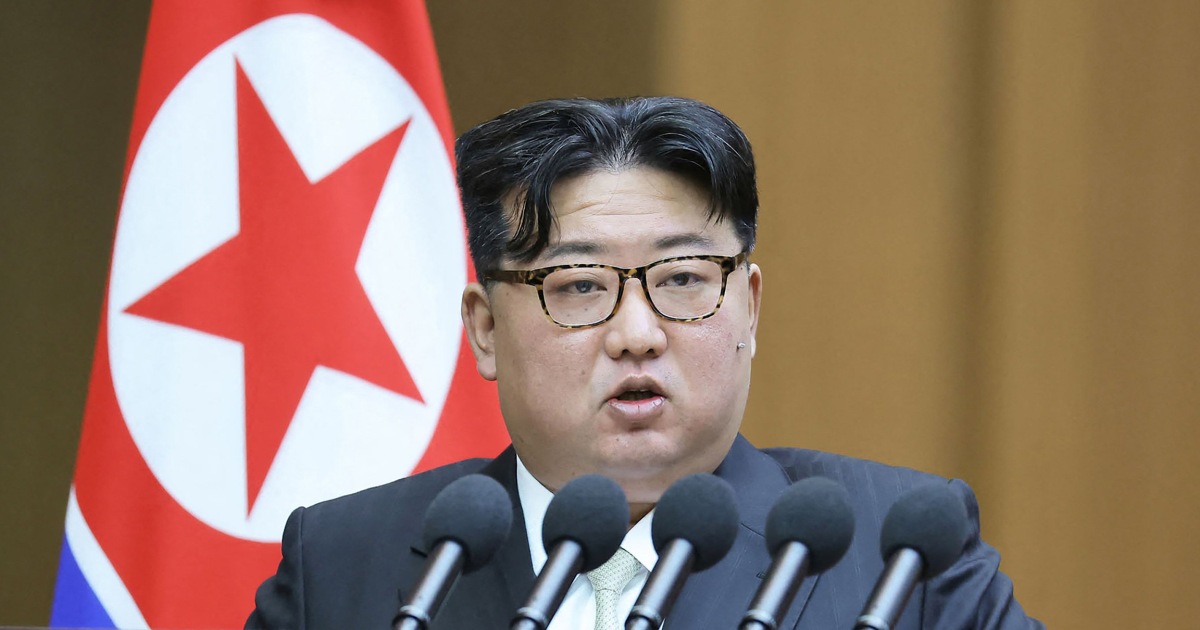
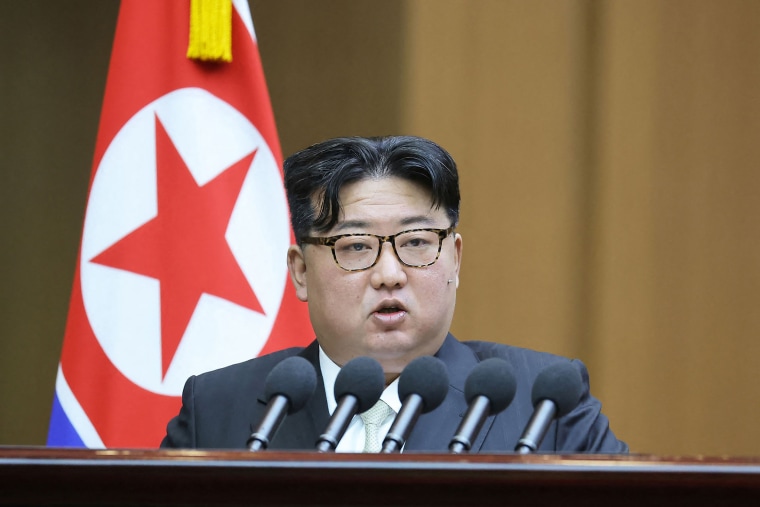
SEOUL, South Korea — North Korean leader Kim Jong Un said his country would no longer pursue reconciliation with South Korea and called for rewriting the North’s constitution to eliminate the idea of shared statehood between the war-divided countries, state media said Tuesday.

The historic step to discard a decades-long pursuit of unification, which was based on a sense of national homogeneity shared by both Koreas, comes amid heightened tensions where the pace of both Kim’s weapons development and the South’s military exercises with the United States have intensified in a tit-for-tat.
North Korea also abolished the key government agencies that had been tasked with managing relations with South Korea in a decision made during a meeting of the country’s rubber-stamp parliament on Monday, the North’s official Korean Central News Agency said.
The Supreme People’s Assembly said the two Koreas are locked in an “acute confrontation” and that it would be a serious mistake for the North to regard the South as a partner in diplomacy.
“The Committee for the Peaceful Reunification of the Country, the National Economic Cooperation Bureau and the (Diamond Mountain) International Tourism Administration, tools which existed for (North-South) dialogue, negotiations and cooperation, are abolished,” the assembly said in a statement.
During a speech at the assembly, Kim blamed South Korea and the United States for raising tensions in the region, citing their expanded joint military exercises, deployments of U.S. strategic military assets, and their trilateral security cooperation with Japan as turning the Korean Peninsula into a dangerous war-risk zone, KCNA said.
Kim said it has become impossible for the North to pursue reconciliation and a peaceful reunification with the South, which he described as “top-class stooges” of outside powers obsessed with confrontational maneuvers.
He called for the assembly to rewrite the North’s constitution to define South Korea as the North’s “primary foe and invariable principal enemy.”
He also ordered the removal of past symbols of inter-Korean reconciliation, to “completely eliminate such concepts as ‘reunification,’ ‘reconciliation’ and ‘fellow countrymen’ from the national history of our republic.”
He specifically demanded cutting off cross-border railway sections and tearing down a monument in Pyongyang honoring the pursuit of reunification, which Kim described as an eyesore.
“It is the final conclusion drawn from the bitter history of the inter-Korean relations that we cannot go along the road of national restoration and reunification together,” he said.
Kim had made similar remarks during a year-end ruling party meeting, saying ties between the Koreas have become “fixed into the relations between two states hostile to each other.” At a political conference last week, he defined South Korea as the North’s “principal enemy” and threatened to annihilate it if provoked.
South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol said during a Cabinet meeting in Seoul that Kim’s comments show the “anti-national and anti-historical” nature of the government in Pyongyang. Yoon said the South was maintaining firm defense readiness and would punish the North “multiple times hard” if it provokes it.
The North’s “fake peace tactic that threatened us to choose between ‘war’ and ‘peace’ no longer works,” Yoon said.
In his speech at the assembly, Kim reiterated that the North has no intention to unilaterally start a war, but has no intentions to avoid one either. Citing his growing military nuclear program, he said a nuclear conflict in the Korean Peninsula would end South Korea’s existence and bring “unimaginable disaster and defeat to the United States.”
The assembly said North Korea’s government would take “practical measures” to implement the decision to abolish the agencies handling dialogue and cooperation with the South.
The National Committee for Peaceful Reunification has been North Korea’s main agency handling inter-Korean affairs since its establishment in 1961.
The National Economic Cooperation Bureau and the Diamond Mountain International Tourism Administration had been set to handle joint economic and tourism projects between the Koreas during a brief period of reconciliation in the 2000s.
Such projects, including a jointly operated factory park in the North Korean border town of Kaesong and South Korean tours to the North’s Diamond Mountain resort, have been halted for years as relations between the rivals worsened over North Korea’s nuclear ambitions.
Those activities are currently banned under U.N. Security Council resolutions against the North that have tightened since 2016 as Kim accelerated his nuclear and missile tests.